652. Find Duplicate SubtreesMedium730151FavoriteShare
Given a binary tree, return all duplicate subtrees. For each kind of duplicate subtrees, you only need to return the root node of any one of them.
Two trees are duplicate if they have the same structure with same node values.
Example 1:
The following are two duplicate subtrees:
1
/ \
2 3
/ / \
4 2 4
/
4
2
/
4
and
4
Therefore, you need to return above trees’ root in the form of a list.
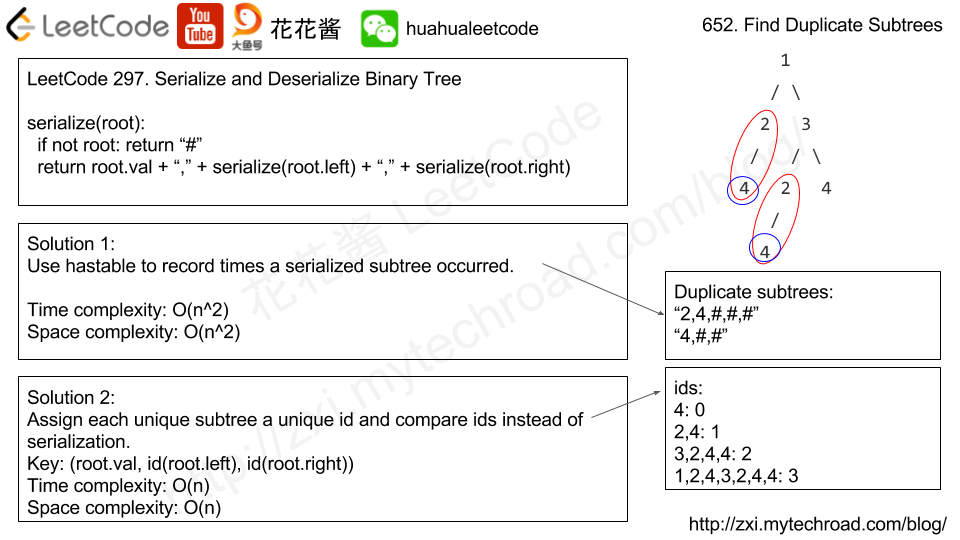
Solution 1: Serialization
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(n^2)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
// Author: Huahua // Runtime: 29 ms class Solution { public: vector<TreeNode*> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode* root) { unordered_map<string, int> counts; vector<TreeNode*> ans; serialize(root, counts, ans); return ans; } private: string serialize(TreeNode* root, unordered_map<string, int>& counts, vector<TreeNode*>& ans) { if (!root) return "#"; string key = to_string(root->val) + "," + serialize(root->left, counts, ans) + "," + serialize(root->right, counts, ans); if (++counts[key] == 2) ans.push_back(root); return key; } }; |
Solution 2: int id for each unique subtree
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
// Author: Huahua // Runtime: 8 ms class Solution { public: vector<TreeNode*> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode* root) { unordered_map<long, pair<int,int>> counts; vector<TreeNode*> ans; getId(root, counts, ans); return ans; } private: int getId(TreeNode* root, unordered_map<long, pair<int,int>>& counts, vector<TreeNode*>& ans) { if (!root) return 0; long key = (static_cast<long>(static_cast<unsigned>(root->val)) << 32) + (getId(root->left, counts, ans) << 16) + getId(root->right, counts, ans); auto& p = counts[key]; if (p.second++ == 0) p.first = counts.size(); else if (p.second == 2) ans.push_back(root); return p.first; } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment