Problem
Design your implementation of the linked list. You can choose to use the singly linked list or the doubly linked list. A node in a singly linked list should have two attributes: val and next. val is the value of the current node, and next is a pointer/reference to the next node. If you want to use the doubly linked list, you will need one more attribute prev to indicate the previous node in the linked list. Assume all nodes in the linked list are 0-indexed.
Implement these functions in your linked list class:
- get(index) : Get the value of the
index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return-1. - addAtHead(val) : Add a node of value
valbefore the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. - addAtTail(val) : Append a node of value
valto the last element of the linked list. - addAtIndex(index, val) : Add a node of value
valbefore theindex-th node in the linked list. Ifindexequals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. - deleteAtIndex(index) : Delete the
index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList(); linkedList.addAtHead(1); linkedList.addAtTail(3); linkedList.addAtIndex(1, 2); // linked list becomes 1->2->3 linkedList.get(1); // returns 2 linkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); // now the linked list is 1->3 linkedList.get(1); // returns 3 |
Note:
- All values will be in the range of
[1, 1000]. - The number of operations will be in the range of
[1, 1000]. - Please do not use the built-in LinkedList library.
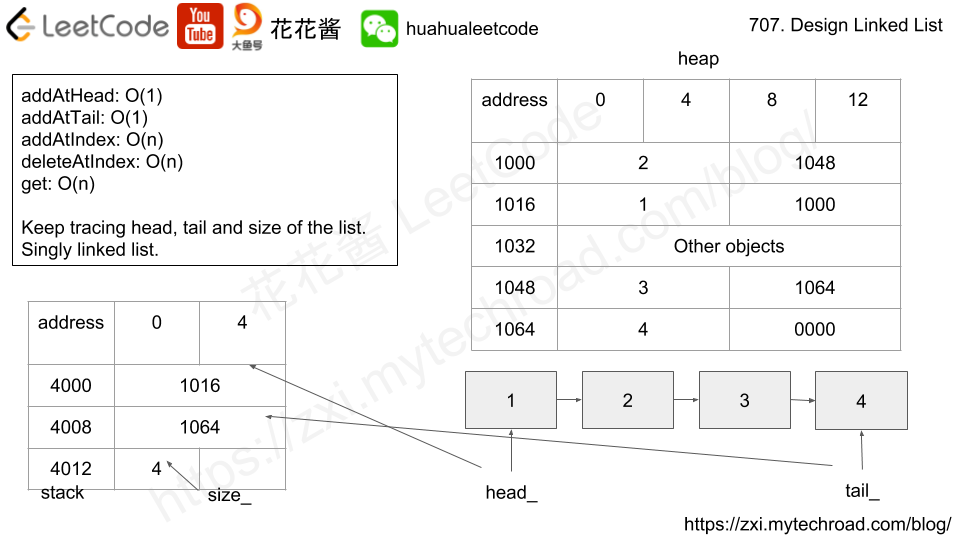
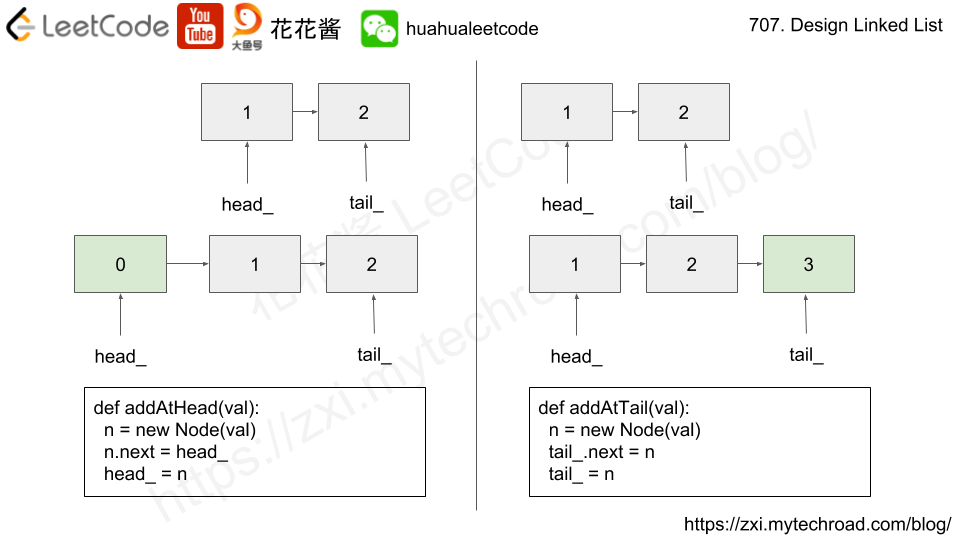
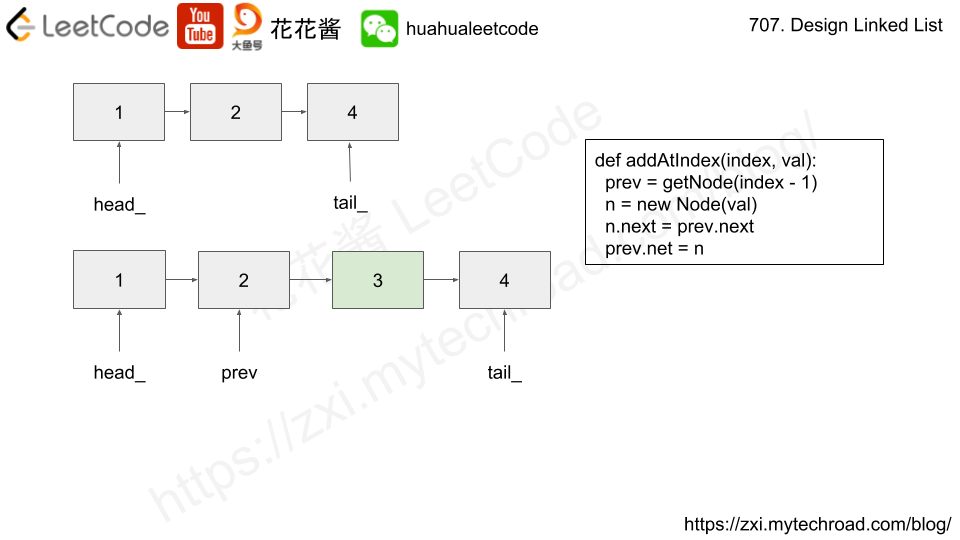
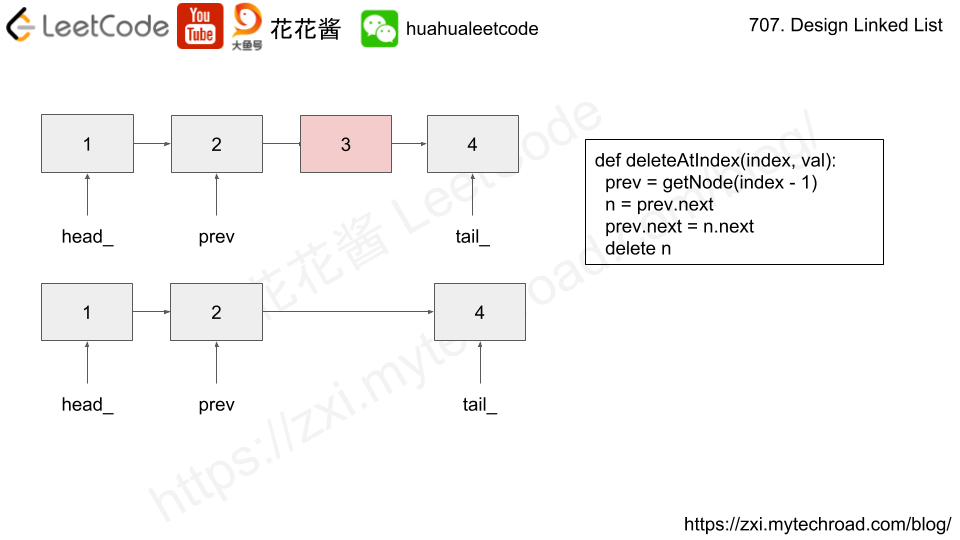
Solution: Single linked list
Keep tracking head and tail of the list.
Time Complexity:
addAtHead, addAtTail O(1)
addAtIndex O(index)
deleteAtIndex O(index)
Space complexity: O(1)
C++
Tracking head/tail and size of the list.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 24 ms class MyLinkedList { public: MyLinkedList(): head_(nullptr), tail_(nullptr), size_(0) {} ~MyLinkedList() { Node* node = head_; while (node) { Node* cur = node; node = node->next; delete cur; } head_ = nullptr; tail_ = nullptr; } int get(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size_) return -1; auto node = head_; while (index--) node = node->next; return node->val; } void addAtHead(int val) { head_ = new Node(val, head_); if (size_++ == 0) tail_ = head_; } void addAtTail(int val) { auto node = new Node(val); if (size_++ == 0) { head_ = tail_ = node; } else { tail_->next = node; tail_ = tail_->next; } } void addAtIndex(int index, int val) { if (index < 0 || index > size_) return; if (index == 0) return addAtHead(val); if (index == size_) return addAtTail(val); Node dummy(0, head_); Node* prev = &dummy; while (index--) prev = prev->next; prev->next = new Node(val, prev->next); ++size_; } void deleteAtIndex(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size_) return; Node dummy(0, head_); Node* prev = &dummy; for (int i = 0; i < index; ++i) prev = prev->next; Node* node_to_delete = prev->next; prev->next = prev->next->next; if (index == 0) head_ = prev->next; if (index == size_ - 1) tail_ = prev; delete node_to_delete; --size_; } private: struct Node { int val; Node* next; Node(int _val): Node(_val, nullptr) {} Node(int _val, Node* _next): val(_val), next(_next) {} }; Node* head_; Node* tail_; int size_; }; |
v2
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 28 ms class MyLinkedList { public: MyLinkedList(): head_(nullptr), tail_(nullptr), dummy_(0), size_(0) {} ~MyLinkedList() { Node* node = head_; while (node) { Node* cur = node; node = node->next; delete cur; } head_ = nullptr; tail_ = nullptr; } int get(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size_) return -1; return getNode(index)->val; } void addAtHead(int val) { head_ = new Node(val, head_); if (size_++ == 0) tail_ = head_; } void addAtTail(int val) { auto node = new Node(val); if (size_++ == 0) { head_ = tail_ = node; } else { tail_->next = node; tail_ = tail_->next; } } void addAtIndex(int index, int val) { if (index < 0 || index > size_) return; if (index == 0) return addAtHead(val); if (index == size_) return addAtTail(val); Node* prev = getNode(index - 1); prev->next = new Node(val, prev->next); ++size_; } void deleteAtIndex(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size_) return; Node* prev = getNode(index - 1); Node* node_to_delete = prev->next; prev->next = node_to_delete->next; if (index == 0) head_ = prev->next; if (index == size_ - 1) tail_ = prev; delete node_to_delete; --size_; } private: struct Node { int val; Node* next; Node(int _val): Node(_val, nullptr) {} Node(int _val, Node* _next): val(_val), next(_next) {} }; Node* head_; // Does not own Node* tail_; // Does not own Node dummy_; int size_; Node* getNode(int index) { dummy_.next = head_; Node* n = &dummy_; for (int i = 0; i <= index; ++i) n = n->next; return n; } }; |
Python3
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
""" Author: Huahua Running time: 132 ms """ class Node: def __init__(self, val, _next=None): self.val = val self.next = _next class MyLinkedList: def __init__(self): self.head = self.tail = None self.size = 0 def getNode(self, index): n = Node(0, self.head) for i in range(index + 1): n = n.next return n def get(self, index): if index < 0 or index >= self.size: return -1 return self.getNode(index).val def addAtHead(self, val): n = Node(val, self.head) self.head = n if self.size == 0: self.tail = n self.size += 1 def addAtTail(self, val): n = Node(val) if self.size == 0: self.head = self.tail = n else: self.tail.next = n self.tail = n self.size += 1 def addAtIndex(self, index, val): if index < 0 or index > self.size: return if index == 0: return self.addAtHead(val) if index == self.size: return self.addAtTail(val) prev = self.getNode(index - 1) n = Node(val, prev.next) prev.next = n self.size += 1 def deleteAtIndex(self, index): if index < 0 or index >= self.size: return prev = self.getNode(index - 1) prev.next = prev.next.next if index == 0: self.head = prev.next if index == self.size - 1: self.tail = prev self.size -= 1 |
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 |
// Author: Huahua // Running time: 74 ms class MyLinkedList { class Node { public int val; public Node next; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; } public Node(int val, Node next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } } private Node head; private Node tail; private int size; public MyLinkedList() { this.head = this.tail = null; this.size = 0; } private Node getNode(int index) { Node n = new Node(0, this.head); while (index-- >= 0) { n = n.next; } return n; } public int get(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) return -1; return getNode(index).val; } public void addAtHead(int val) { this.head = new Node(val, this.head); if (this.size++ == 0) this.tail = this.head; } public void addAtTail(int val) { Node n = new Node(val); if (this.size++ == 0) this.head = this.tail = n; else this.tail = this.tail.next = n; } public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) { if (index < 0 || index > this.size) return; if (index == 0) { this.addAtHead(val); return; } if (index == size) { this.addAtTail(val); return; } Node prev = this.getNode(index - 1); prev.next = new Node(val, prev.next); ++this.size; } public void deleteAtIndex(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) return; Node prev = this.getNode(index - 1); prev.next = prev.next.next; if (index == 0) this.head = prev.next; if (index == this.size - 1) this.tail = prev; --this.size; } } |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment