There are n friends that are playing a game. The friends are sitting in a circle and are numbered from 1 to n in clockwise order. More formally, moving clockwise from the ith friend brings you to the (i+1)th friend for 1 <= i < n, and moving clockwise from the nth friend brings you to the 1st friend.
The rules of the game are as follows:
- Start at the
1stfriend. - Count the next
kfriends in the clockwise direction including the friend you started at. The counting wraps around the circle and may count some friends more than once. - The last friend you counted leaves the circle and loses the game.
- If there is still more than one friend in the circle, go back to step
2starting from the friend immediately clockwise of the friend who just lost and repeat. - Else, the last friend in the circle wins the game.
Given the number of friends, n, and an integer k, return the winner of the game.
Example 1:
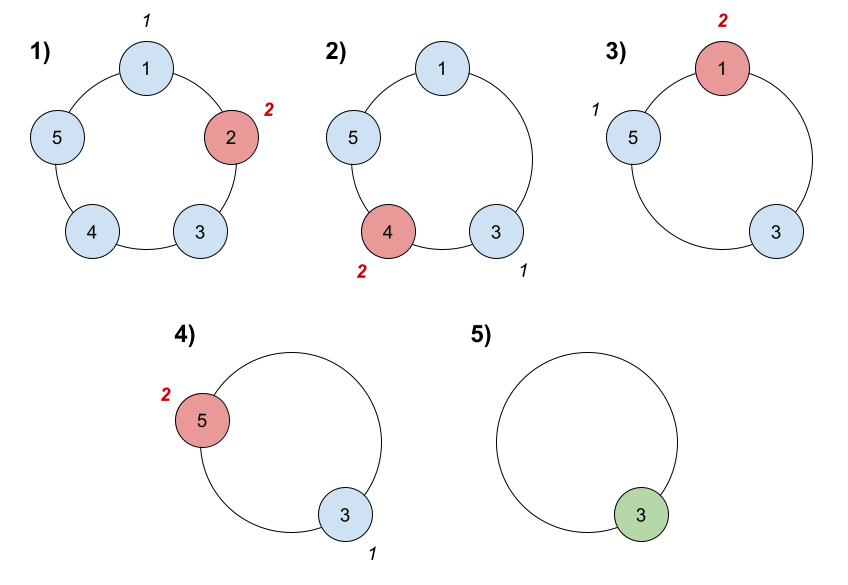
Input: n = 5, k = 2 Output: 3 Explanation: Here are the steps of the game: 1) Start at friend 1. 2) Count 2 friends clockwise, which are friends 1 and 2. 3) Friend 2 leaves the circle. Next start is friend 3. 4) Count 2 friends clockwise, which are friends 3 and 4. 5) Friend 4 leaves the circle. Next start is friend 5. 6) Count 2 friends clockwise, which are friends 5 and 1. 7) Friend 1 leaves the circle. Next start is friend 3. 8) Count 2 friends clockwise, which are friends 3 and 5. 9) Friend 5 leaves the circle. Only friend 3 is left, so they are the winner.
Example 2:
Input: n = 6, k = 5 Output: 1 Explanation: The friends leave in this order: 5, 4, 6, 2, 3. The winner is friend 1.
Constraints:
1 <= k <= n <= 500
Solution 1: Simulation w/ Queue / List
Time complexity: O(n*k)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++/Queue
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
// Author: Huahua, 56 ms, 24.3 MB class Solution { public: int findTheWinner(int n, int k) { queue<int> q; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) q.push(i); while (q.size() != 1) { for (int i = 1; i < k; ++i) { int x = q.front(); q.pop(); q.push(x); } q.pop(); } return q.front(); } }; |
C++/List
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
// Author: Huahua, 12 ms, 6.8 MB class Solution { public: int findTheWinner(int n, int k) { list<int> l; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) l.push_back(i); auto it = l.begin(); while (l.size() != 1) { for (int i = 1; i < k; ++i) if (++it == l.end()) it = l.begin(); it = l.erase(it); if (it == l.end()) it = l.begin(); } return l.front(); } }; |