There is an undirected weighted connected graph. You are given a positive integer n which denotes that the graph has n nodes labeled from 1 to n, and an array edges where each edges[i] = [ui, vi, weighti] denotes that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi with weight equal to weighti.
A path from node start to node end is a sequence of nodes [z0, z1,z2, ..., zk] such that z0 = start and zk = end and there is an edge between zi and zi+1 where 0 <= i <= k-1.
The distance of a path is the sum of the weights on the edges of the path. Let distanceToLastNode(x) denote the shortest distance of a path between node n and node x. A restricted path is a path that also satisfies that distanceToLastNode(zi) > distanceToLastNode(zi+1) where 0 <= i <= k-1.
Return the number of restricted paths from node 1 to node n. Since that number may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
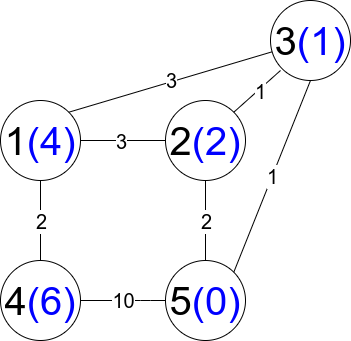
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[2,3,1],[1,4,2],[5,2,2],[3,5,1],[5,4,10]]
Output: 3
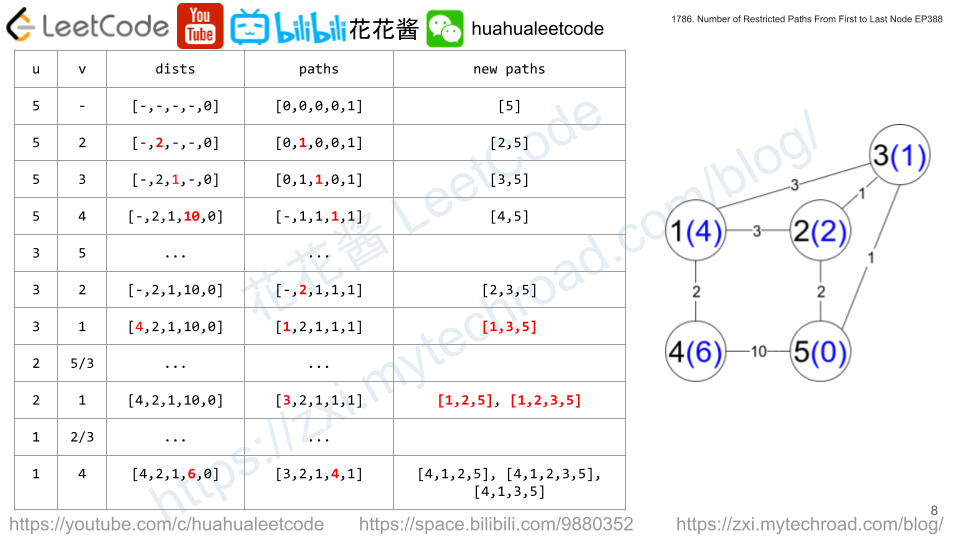
Explanation: Each circle contains the node number in black and its distanceToLastNode value in blue. The three restricted paths are:
1) 1 --> 2 --> 5
2) 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 5
3) 1 --> 3 --> 5
Example 2:
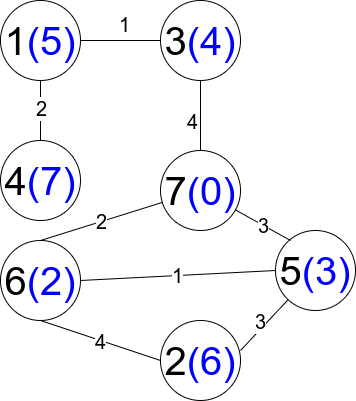
Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,3,1],[4,1,2],[7,3,4],[2,5,3],[5,6,1],[6,7,2],[7,5,3],[2,6,4]]
Output: 1
Explanation: Each circle contains the node number in black and its distanceToLastNode value in blue. The only restricted path is 1 --> 3 --> 7.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 104n - 1 <= edges.length <= 4 * 104edges[i].length == 31 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi1 <= weighti <= 105- There is at most one edge between any two nodes.
- There is at least one path between any two nodes.
Solution: Dijkstra + DFS w/ memoization
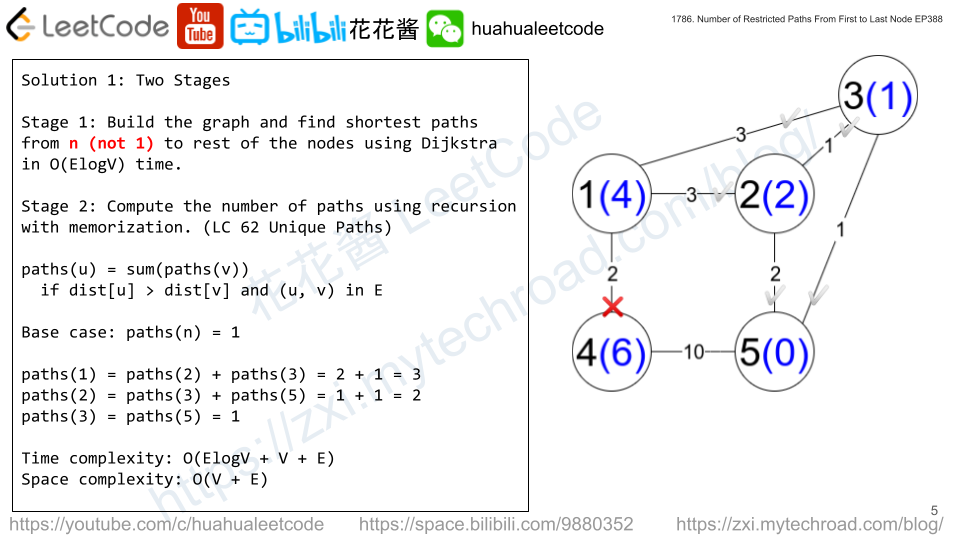
Find shortest path from n to all the nodes.
paths(u) = sum(paths(v)) if dist[u] > dist[v] and (u, v) has an edge
return paths(1)
Time complexity: O(ElogV + V + E)
Space complexity: O(V + E)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int countRestrictedPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { constexpr int kMod = 1e9 + 7; using PII = pair<int, int>; vector<vector<PII>> g(n + 1); for (const auto& e : edges) { g[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1], e[2]); g[e[1]].emplace_back(e[0], e[2]); } // Shortest distance from n to x. vector<int> dist(n + 1, INT_MAX / 2); dist[n] = 0; priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, std::greater<PII>> q; q.emplace(0, n); while (!q.empty()) { const auto [d, u] = q.top(); q.pop(); if (dist[u] < d) continue; for (auto [v, w]: g[u]) { if (dist[u] + w >= dist[v]) continue; dist[v] = dist[u] + w; q.emplace(dist[v], v); } } vector<int> dp(n + 1, INT_MAX); function<int(int)> dfs = [&](int u) { if (u == n) return 1; if (dp[u] != INT_MAX) return dp[u]; int ans = 0; for (auto [v, w]: g[u]) if (dist[u] > dist[v]) ans = (ans + dfs(v)) % kMod; return dp[u] = ans; }; return dfs(1); } }; |
Combined
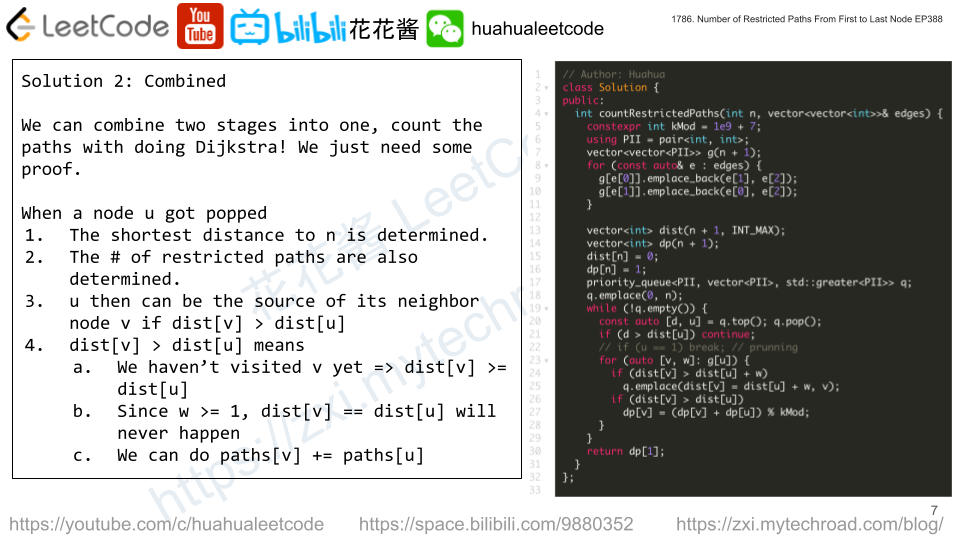
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: int countRestrictedPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { constexpr int kMod = 1e9 + 7; using PII = pair<int, int>; vector<vector<PII>> g(n + 1); for (const auto& e : edges) { g[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1], e[2]); g[e[1]].emplace_back(e[0], e[2]); } // Shortest distance from n to x. vector<int> dist(n + 1, INT_MAX); vector<int> dp(n + 1); dist[n] = 0; dp[n] = 1; priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, std::greater<PII>> q; q.emplace(0, n); while (!q.empty()) { const auto [d, u] = q.top(); q.pop(); if (d > dist[u]) continue; if (u == 1) break; for (auto [v, w]: g[u]) { if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) q.emplace(dist[v] = dist[u] + w, v); if (dist[v] > dist[u]) dp[v] = (dp[v] + dp[u]) % kMod; } } return dp[1]; } }; |