Given the array prices where prices[i] is the price of the ith item in a shop. There is a special discount for items in the shop, if you buy the ith item, then you will receive a discount equivalent to prices[j] where j is the minimum index such that j > i and prices[j] <= prices[i], otherwise, you will not receive any discount at all.
Return an array where the ith element is the final price you will pay for the ith item of the shop considering the special discount.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [8,4,6,2,3] Output: [4,2,4,2,3] Explanation: For item 0 with price[0]=8 you will receive a discount equivalent to prices[1]=4, therefore, the final price you will pay is 8 - 4 = 4. For item 1 with price[1]=4 you will receive a discount equivalent to prices[3]=2, therefore, the final price you will pay is 4 - 2 = 2. For item 2 with price[2]=6 you will receive a discount equivalent to prices[3]=2, therefore, the final price you will pay is 6 - 2 = 4. For items 3 and 4 you will not receive any discount at all.
Example 2:
Input: prices = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [1,2,3,4,5] Explanation: In this case, for all items, you will not receive any discount at all.
Example 3:
Input: prices = [10,1,1,6] Output: [9,0,1,6]
Constraints:
1 <= prices.length <= 5001 <= prices[i] <= 10^3
Solution 1: Simulation
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(1)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: vector<int> finalPrices(vector<int> prices) { const int n = prices.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) if (prices[j] <= prices[i]) { prices[i] -= prices[j]; break; } return prices; } }; |
Solution 2: Monotonic Stack
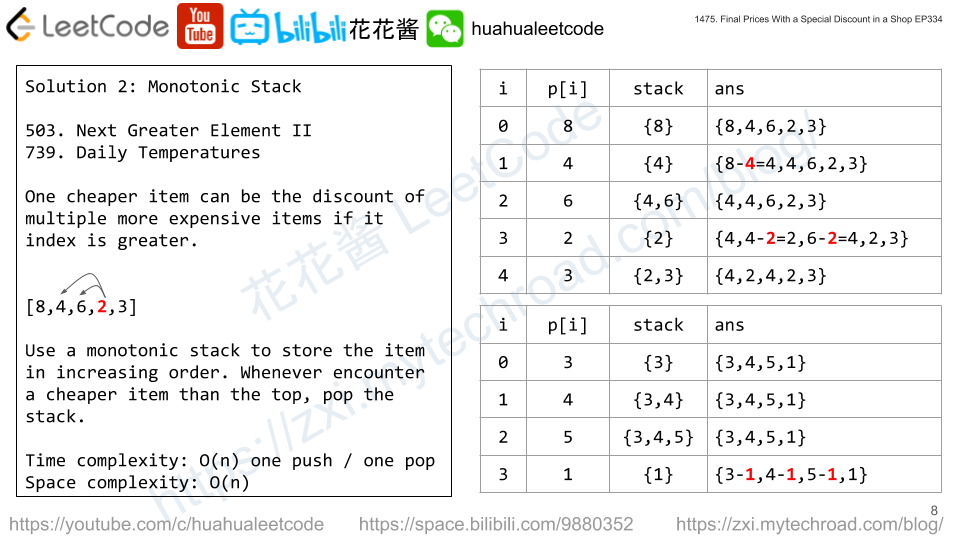
Use a stack to store monotonically increasing items, when the current item is cheaper than the top of the stack, we get the discount and pop that item. Repeat until the current item is no longer cheaper or the stack becomes empty.
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: vector<int> finalPrices(vector<int> prices) { // stores pointers of monotonically incraseing elements. stack<int*> s; for (int& p : prices) { while (!s.empty() && *s.top() >= p) { *s.top() -= p; s.pop(); } s.push(&p); } return prices; } }; |
index version
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: vector<int> finalPrices(vector<int> prices) { // stores indices of monotonically incraseing elements. stack<int> s; for (int i = 0; i < prices.size(); ++i) { while (!s.empty() && prices[s.top()] >= prices[i]) { prices[s.top()] -= prices[i]; s.pop(); } s.push(i); } return prices; } }; |
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!花花保留对文章/视频的所有权利。
如果您喜欢这篇文章/视频,欢迎您捐赠花花。
If you like my articles / videos, donations are welcome.



Be First to Comment