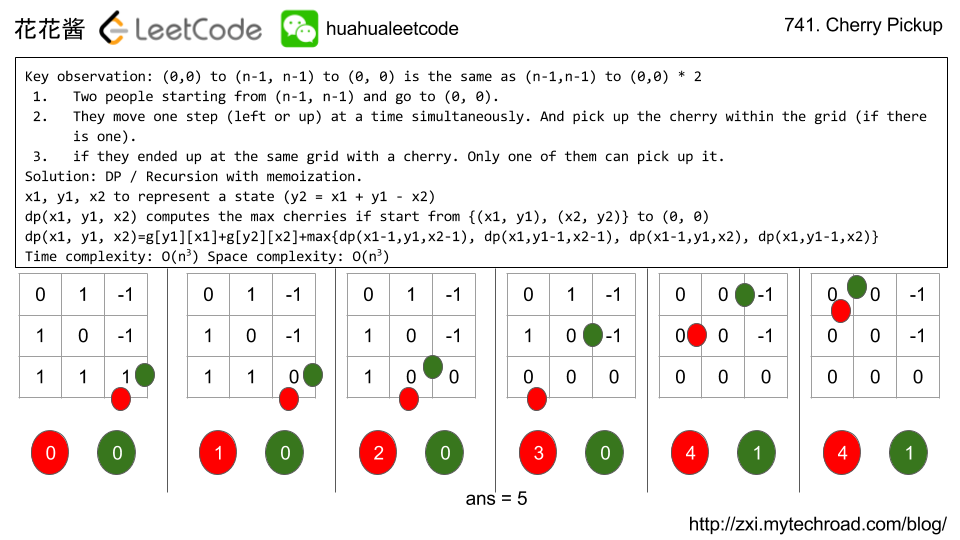
题目大意:给你樱桃田的地图(1: 樱桃, 0: 空, -1: 障碍物)。然你从左上角走到右下角(只能往右或往下),再从右下角走回左上角(只能往左或者往上)。问你最多能采到多少棵樱桃。
Problem:
In a N x N grid representing a field of cherries, each cell is one of three possible integers.
- 0 means the cell is empty, so you can pass through;
- 1 means the cell contains a cherry, that you can pick up and pass through;
- -1 means the cell contains a thorn that blocks your way.
Your task is to collect maximum number of cherries possible by following the rules below:
- Starting at the position (0, 0) and reaching (N-1, N-1) by moving right or down through valid path cells (cells with value 0 or 1);
- After reaching (N-1, N-1), returning to (0, 0) by moving left or up through valid path cells;
- When passing through a path cell containing a cherry, you pick it up and the cell becomes an empty cell (0);
- If there is no valid path between (0, 0) and (N-1, N-1), then no cherries can be collected.
Example 1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
Input: grid = [[0, 1, -1], [1, 0, -1], [1, 1, 1]] Output: 5 Explanation: The player started at (0, 0) and went down, down, right right to reach (2, 2). 4 cherries were picked up during this single trip, and the matrix becomes [[0,1,-1],[0,0,-1],[0,0,0]]. Then, the player went left, up, up, left to return home, picking up one more cherry. The total number of cherries picked up is 5, and this is the maximum possible. |
Note:
gridis anNbyN2D array, with1 <= N <= 50.- Each
grid[i][j]is an integer in the set{-1, 0, 1}. - It is guaranteed that grid[0][0] and grid[N-1][N-1] are not -1.
Idea:
DP
Key observation: (0,0) to (n-1, n-1) to (0, 0) is the same as (n-1,n-1) to (0,0) twice
- Two people starting from (n-1, n-1) and go to (0, 0).
- They move one step (left or up) at a time simultaneously. And pick up the cherry within the grid (if there is one).
- if they ended up at the same grid with a cherry. Only one of them can pick up it.
Solution: DP / Recursion with memoization.
x1, y1, x2 to represent a state y2 can be computed: y2 = x1 + y1 – x2
dp(x1, y1, x2) computes the max cherries if start from {(x1, y1), (x2, y2)} to (0, 0), which is a recursive function.
Since two people move independently, there are 4 subproblems: (left, left), (left, up), (up, left), (left, up). Finally, we have:
dp(x1, y1, x2)= g[y1][x1] + g[y2][x2] + max{dp(x1-1,y1,x2-1), dp(x1,y1-1,x2-1), dp(x1-1,y1,x2), dp(x1,y1-1,x2)}
Time complexity: O(n^3)
Space complexity: O(n^3)
Solution: DP
Time complexity: O(n^3)
Space complexity: O(n^3)
C ++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
// Author: Huahua // Runtime: 32 ms class Solution { public: int cherryPickup(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { const int n = grid.size(); grid_ = &grid; m_ = vector<vector<vector<int>>>( n, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(n, INT_MIN))); return max(0, dp(n - 1, n - 1, n - 1)); } private: // max cherries from (x1, y1) to (0, 0) + (x2, y2) to (0, 0) int dp(int x1, int y1, int x2) { const int y2 = x1 + y1 - x2; if (x1 < 0 || y1 < 0 || x2 < 0 || y2 < 0) return -1; if ((*grid_)[y1][x1] < 0 || (*grid_)[y2][x2] < 0) return -1; if (x1 == 0 && y1 == 0) return (*grid_)[y1][x1]; if (m_[x1][y1][x2] != INT_MIN) return m_[x1][y1][x2]; int ans = max(max(dp(x1 - 1, y1, x2 - 1), dp(x1, y1 - 1, x2)), max(dp(x1, y1 - 1, x2 - 1), dp(x1 - 1, y1, x2))); if (ans < 0) return m_[x1][y1][x2] = -1; ans += (*grid_)[y1][x1]; if (x1 != x2) ans += (*grid_)[y2][x2]; return m_[x1][y1][x2] = ans; } vector<vector<vector<int>>> m_; vector<vector<int>>* grid_; // does not own the object }; |
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { private int[][] grid; private int[][][] memo; public int cherryPickup(int[][] grid) { this.grid = grid; int m = grid.length; int n = grid[0].length; memo = new int[m][n][n]; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) Arrays.fill(memo[i][j], Integer.MIN_VALUE); return Math.max(0, dp(n - 1, m - 1, n - 1)); } private int dp(int x1, int y1, int x2) { final int y2 = x1 + y1 - x2; if (x1 < 0 || y1 < 0 || x2 < 0 || y2 < 0) return -1; if (grid[y1][x1] < 0 || grid[y2][x2] < 0) return -1; if (x1 == 0 && y1 == 0) return grid[y1][x1]; if (memo[y1][x1][x2] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) return memo[y1][x1][x2]; memo[y1][x1][x2] = Math.max(Math.max(dp(x1 - 1, y1, x2 - 1), dp(x1, y1 - 1, x2)), Math.max(dp(x1, y1 - 1, x2 - 1), dp(x1 - 1, y1, x2))); if (memo[y1][x1][x2] >= 0) { memo[y1][x1][x2] += grid[y1][x1]; if (x1 != x2) memo[y1][x1][x2] += grid[y2][x2]; } return memo[y1][x1][x2]; } } |
Related Problems: