You are given two strings a and b of the same length. Choose an index and split both strings at the same index, splitting a into two strings: aprefix and asuffix where a = aprefix + asuffix, and splitting b into two strings: bprefix and bsuffix where b = bprefix + bsuffix. Check if aprefix + bsuffix or bprefix + asuffix forms a palindrome.
When you split a string s into sprefix and ssuffix, either ssuffix or sprefix is allowed to be empty. For example, if s = "abc", then "" + "abc", "a" + "bc", "ab" + "c" , and "abc" + "" are valid splits.
Return true if it is possible to form a palindrome string, otherwise return false.
Notice that x + y denotes the concatenation of strings x and y.
Example 1:
Input: a = "x", b = "y" Output: true Explaination: If either a or b are palindromes the answer is true since you can split in the following way: aprefix = "", asuffix = "x" bprefix = "", bsuffix = "y" Then, aprefix + bsuffix = "" + "y" = "y", which is a palindrome.
Example 2:
Input: a = "abdef", b = "fecab" Output: true
Example 3:
Input: a = "ulacfd", b = "jizalu" Output: true Explaination: Split them at index 3: aprefix = "ula", asuffix = "cfd" bprefix = "jiz", bsuffix = "alu" Then, aprefix + bsuffix = "ula" + "alu" = "ulaalu", which is a palindrome.
Example 4:
Input: a = "xbdef", b = "xecab" Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= a.length, b.length <= 105a.length == b.lengthaandbconsist of lowercase English letters
Solution: Greedy
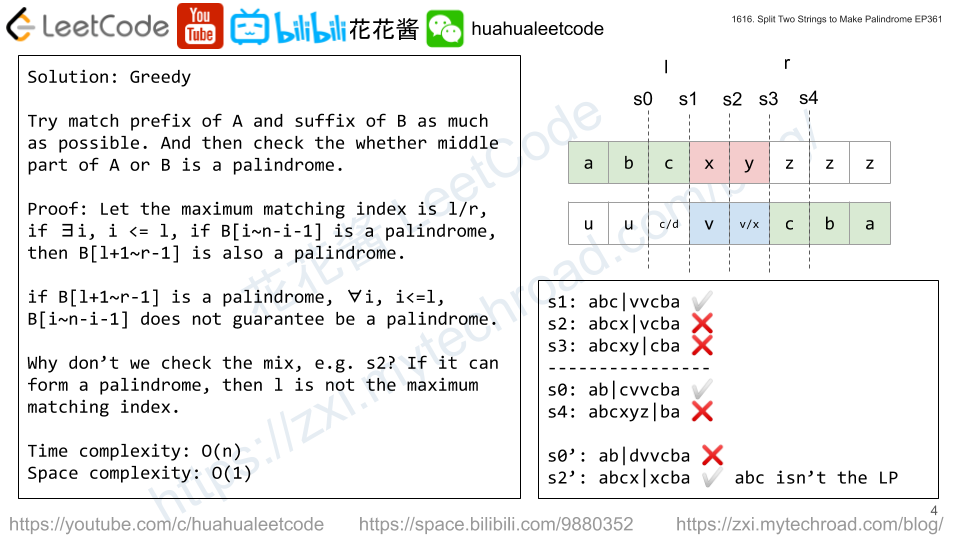
Try to match the prefix of A and suffix of B (or the other way) as much as possible and then check whether the remaining part is a palindrome or not.
e.g. A = “abcxyzzz”, B = “uuuvvcba”
A’s prefix abc matches B’s suffix cba
We just need to check whether “xy” or “vv” is palindrome or not.
The concatenated string “abc|vvcba” is a palindrome, left abc is from A and vvcba is from B.
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
// Author: Huahua class Solution { public: bool checkPalindromeFormation(string a, string b) { auto isPalindrome = [](const string& s, int i, int j) { while (i < j && s[i] == s[j]) ++i, --j; return i >= j; }; auto check = [&isPalindrome](const string& a, const string& b) { int i = 0; int j = a.length() - 1; while (a[i] == b[j]) ++i, --j; return isPalindrome(a, i, j) || isPalindrome(b, i, j); }; return check(a, b) || check(b, a); } }; |